does ketoacidosis go away Ketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic diabetic inhibitor induced pathophysiology dka urine renalfellow renal sediment mitochondria acidosis immunologic transplantation principles bacterial variant
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when your body starts breaking down fat for energy instead of glucose, leading to a buildup of ketones in your blood. Symptoms of DKA include frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment for DKA typically involves hydration with fluids and electrolytes, insulin therapy, and close monitoring of blood sugar and ketones levels. There are also several treatments available for preventing DKA in individuals with diabetes. These include monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, taking insulin as prescribed, and following a healthy diet and exercise routine. Another potential risk factor for DKA is the use of SGLT2 inhibitors, a class of medications commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes. SGLT2 inhibitors work by preventing the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased excretion of glucose in the urine. While these medications can be effective in controlling blood sugar levels, they can also increase the risk of euglycemic DKA. Euglycemic DKA is a rare but serious condition in which blood sugar levels remain normal or near normal, despite the presence of ketones in the blood. This can make it difficult to diagnose, as many individuals may not realize they are at risk until they experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. If you are taking an SGLT2 inhibitor, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of euglycemic DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms. Your healthcare provider may also recommend monitoring your blood sugar and ketone levels regularly, especially if you are at higher risk of developing the condition. In addition to medical treatments and preventative measures, there are several lifestyle changes that can help manage and prevent DKA in individuals with diabetes. These include maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, reducing stress, and getting regular exercise. While DKA can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, it is important to remember that with proper treatment and preventative measures, it is possible to manage and live a healthy life with diabetes. If you or someone you know is at risk of developing DKA or has already been diagnosed with the condition, speak with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and guidance.
If you are searching about SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow Network you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pics about SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow Network like Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hypersmolar Non-ketotic coma - Endocrinology Advisor, SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow Network and also Diabetes and Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment. Here you go:
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow Network
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic diabetic inhibitor induced pathophysiology dka urine renalfellow renal sediment mitochondria acidosis immunologic transplantation principles bacterial variant
Diabetic Ketoacidosis And Hypersmolar Non-ketotic Coma - Endocrinology Advisor
 www.endocrinologyadvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic coma ketotic hhs pathophysiology hyperglycemia acidosis metabolism
www.endocrinologyadvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic coma ketotic hhs pathophysiology hyperglycemia acidosis metabolism
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Detailed Explanation Within 7 Minutes | Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Diabetes
 www.pinterest.comketoacidosis diabetic explanation ketone bodies
www.pinterest.comketoacidosis diabetic explanation ketone bodies
Diabetic Exchange: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatments
 diabeticexchange.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic diabetes dka nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body treatments
diabeticexchange.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic diabetes dka nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body treatments
Diabetes And Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment
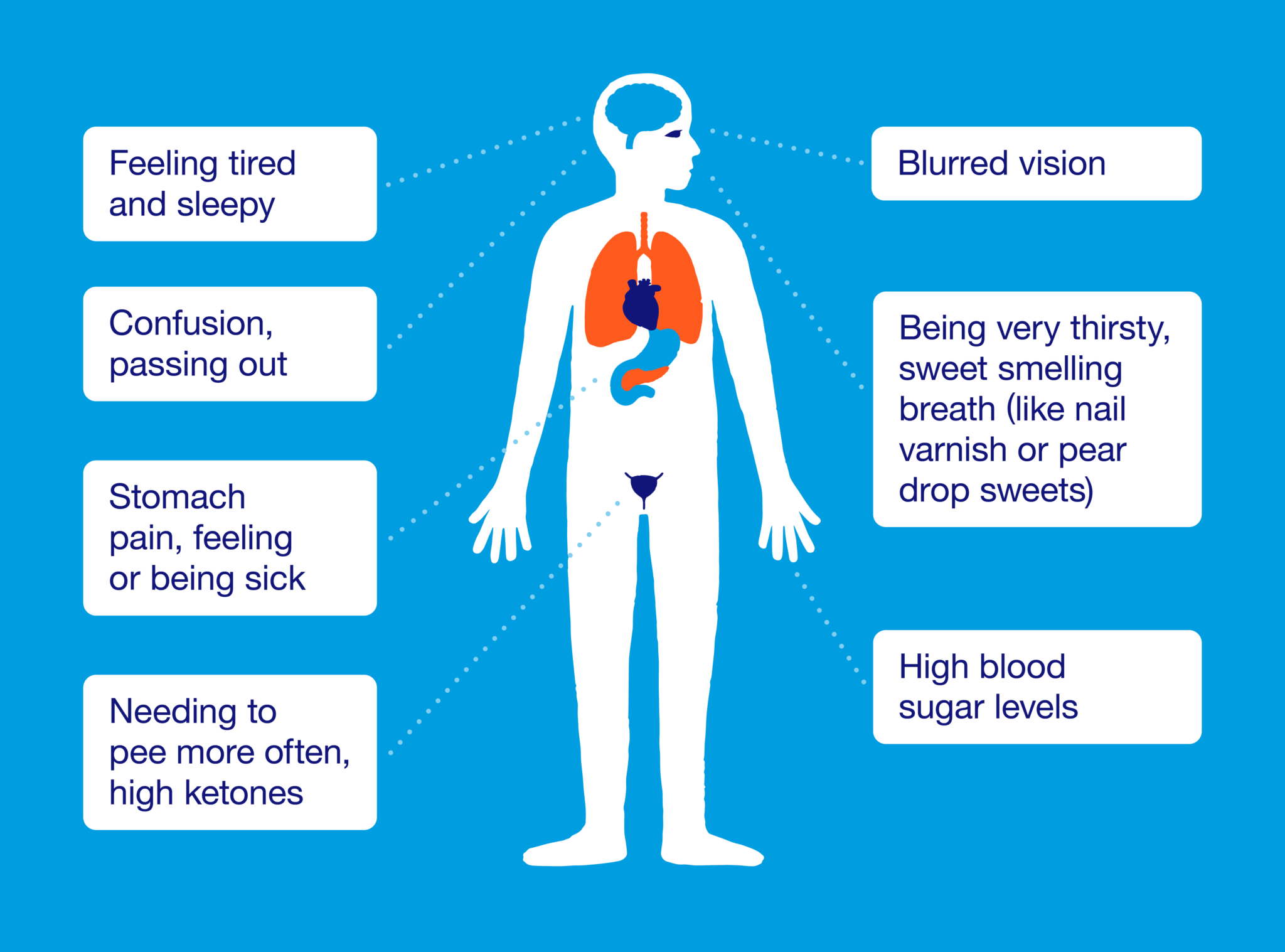 mantracare.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka breath treatment complications fruity ketosis symptome mellitus ketones urine mantracare anzeichen abdominal ursachen nausea difficulty remedies
mantracare.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka breath treatment complications fruity ketosis symptome mellitus ketones urine mantracare anzeichen abdominal ursachen nausea difficulty remedies
Ketoacidosis diabetic dka breath treatment complications fruity ketosis symptome mellitus ketones urine mantracare anzeichen abdominal ursachen nausea difficulty remedies. Ketoacidosis diabetic explanation ketone bodies. Diabetic ketoacidosis detailed explanation within 7 minutes